Research Highlights: School of Soil Stress Management
- Technologies developed under School of Soil Stress Management
- Process for synthesis of bactericidal silver nanoparticles using fishery waste.(Patent 3255/MUM/2012 Journal No. 30/2014)
- Microbial derived polymeric product for gel formation, microbial colonization and metals binding. (Patent Application No 3127/MUM/2015)
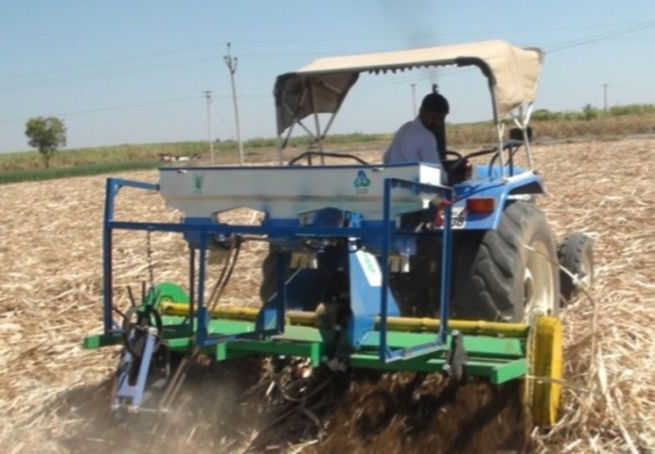
- A stubble shaver, off bar cum fertilizer applicator upgraded with the inclusion of larger capacity fertilizer box and root pruning mechanism for improving the cane yield and N-use efficiency of sugarcane ratoon crop under surface retention of trash
- Metagenomic protocol for examining unculturable microbial diversity of saline soils
- Hapa culture of fish using intermediary water of agriculture
- Breeding and seed production of air breathing catfish Heteropneustes fossilis (Shinghi) in Western Maharashtra
- Standardization of extraction protocol for crude biomolecules from bacterial isolate using XAD-16
- Zeolite trapped with silver nanopaprticles for ammonia removal and bactericidal activity
- Standardization of rapid method for quantitative detection of IAA and IBA
- Protocol for assessing multiple heavy metals in aquatic water body
- Biological synthesis of selenium and zinc nanoparticles
- Integrated agri-aquaculture (Concept)
- Improving nitrogen-use efficiency through N application methods under surface retention of trash
Adoption of individual or in combination of sugarcane ratoon management practices like surface retention of chopped trash, stubble shaving, off-barring, root pruning and placement of fertilisers in soil with the use of SORF machine improved the cane yield by 14-38% over un-chopped trash and broadcast application of fertilisers.
Band placement of either recommended or doubles the dose of N as basal rather than recommended two splits as basal and at earthing-up through broadcasting increased the net profit of farmers by Rs. 27-50 thousand/ha and broadcast application of fertilisers ratio up to 12.6 % over farmer’s practice.
A stubble shaver, off bar cum fertilizer applicator developed by IISR, Lucknow and further upgraded with the inclusion of larger capacity fertilizer box and root pruning mechanism. Beneficial in improving the cane yield and N-use efficiency of sugarcane ratoon crop.



- Protocol for evaluating lignin degrading bacteria
A UHPLC based protocol has been standardized for evaluating lignin degrading bacteria. Heterotrophic bacteria have been isolated from biogas slurry and further characterized using 16S
rRNA gene approach
|
Organism Identity |
Accession no. |
Guaiacylglycerol-β-guaiacyl ether (Lignin dimer) |
|
Citrobacter freundii A1b |
KR006908 |
|
|
Klebsiella pnuemoniae A2 |
KR006909 |
|
|
Klebsiella pneumonia B |
KR006910 |
|
|
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia A4 |
KR006911 |
|
|
Ochrabactrum sp C |
KR006912 |
|
|
Ochrabactrum grignonense D |
KR006913 |
|
|
Ochrabactrum gallinifaecis S |
KR006914 |
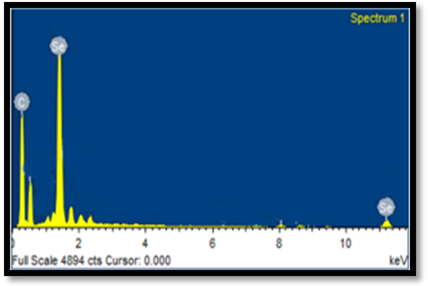
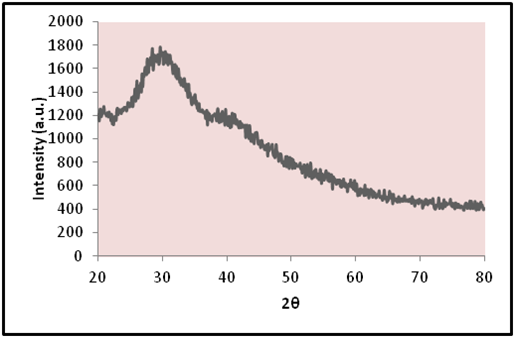
- Process for the synthesis of nanostructured materials using fisheries wastes
(Patent 3255/MUM/2012 Journal No. 30/2014)
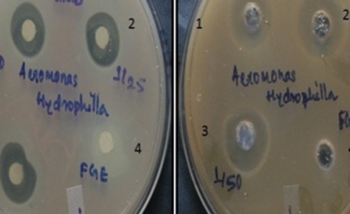
Synthesis of nanoparticles is an important component of the rapidly growing research efforts in nanoscience and nanoengineering. One step process has been developed for the synthesis of silver, zinc and selenium nano particles using fisheries wastes. The nanostructured materials have been characterized by SEM-EDAX, TEM and XRD. This invention further relates to application of such synthesized bactericidal nanoparticles for controlling fish pathogens such as Aeromonas hydrophila in aquaculture.
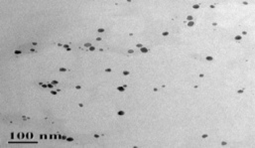

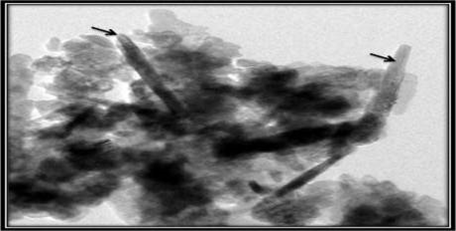
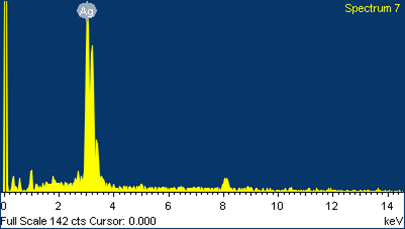
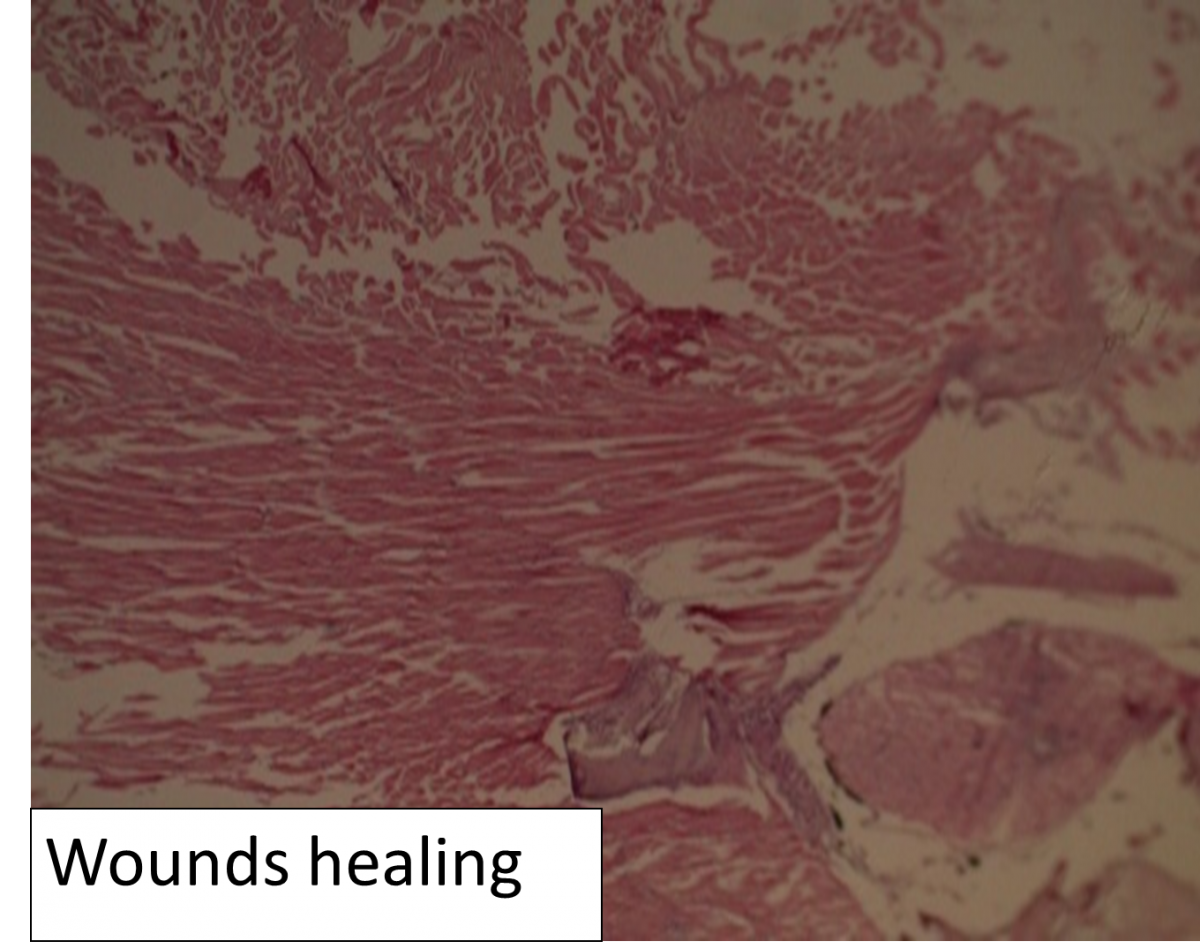
Feed additive as anti-infection candidate in fish (Wound healing agent)

- Nano(bio-)remediation for alleviation of multiple abiotic and biotic stressors
Novel nanoparticles and its role in environmental remediation is the subject of extensive research. Nanomaterials have increasingly been used in water treatment because of economical and environmental viability and wider availability. Abundantly available zeolites in quarries of Maharashtra and modifications of the surface and pores of zeolites make them attractive candidates for various applications. Thirteen different forms of zeolites such as Mesolite, Thaumarite, Okenite, Mordanite, Prehnite, Thomsonite, Gyrolite, Scolerite, Stilbite, Heulandite, Stellerite, Apophyllite and Ferrerite were subjected to trapping of silver nanoparticles and native zeolites and zeolites trapped with silver nano particles were characterized by ICP-MS, which indicated the trapping of silver nanoparticles in zeolites. This has potential application in alleviation of multiple stressors in aquaculture system viz ammonia removal and bactericidal activity.





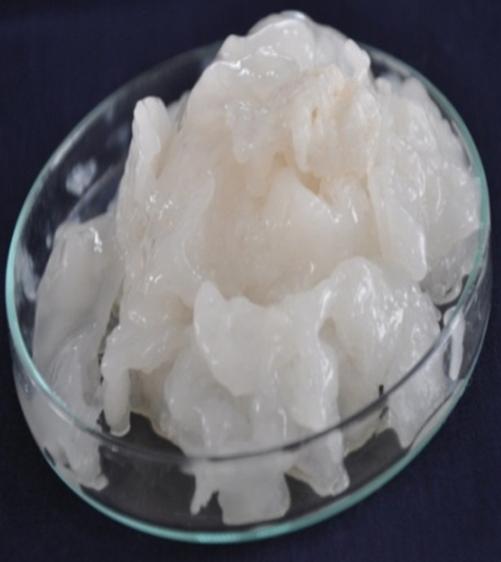
- Microbially derived polymeric product for gel formation, microbial colonisation and metals binding
Present invention relates to the development of low cost microbially derived polymeric product. The said product has considerably high binding capacity with monovalent and bivalent cations due to the presence of multiple functional groups. The product serve as an immobilizing matrix through the formation of biofilm and nurturing root microbial colonization as it has high surface area and longer retention time and protection from inhibitory compounds for maintenance of a high microbial cell density and optimization of microbial growth. The product acts as a good gelling agent due to its water holding capacity. This invention has an application in gel formation for slow delivery, microbial colonization through biofilm formation and the binding of toxic heavy metals and other metallic cations including alkali and alkaline earth metals.
AMAAS 13 (LC027458 Rhizobium sp. NIASMXIII from Psoralea corylifolia L.) Babchi



- Protocol for assessment of heavy metals in aquatic bodies
ICP-MS based protocol has been standardized for assessment of multiple metals such as Li, Be, Na, Mg, Al, K, Ca, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ga, As, Se, Rb, Sr, Cd, Cs, Sn. Sb, Hg, Pb, Bi and U in the surface water, soil sediments and fish tissues samples viz. gill, liver, kidney, muscle and gonad. In addition, enzyme based protocols have been standardized as biomarkers for monitoring heavy metals contamination in aquatic water bodies.
Hapa culture of fish using intermediary water of agriculture


Breeding and seed production of air breathing catfish Heteropneustes fossilis (shinghi) in Western Maharashtra



- Examination of unculturable microbial diversity of saline soils using metagenomics
For the first time, method for creation of metagenomic clone library for examination of microbial diversity of salt effected soils of Maharashtra has successfully been standardized with the result of submission of sixteen sequences of 16S rRNA metagenomic clones in NCBI Gene Bank database, which can be retrieved with following accessions KJ561578 to KJ561585 (8 sequences) &KJ638401 to KJ638408 (8 Sequences). Out of 16 sequences, five sequences were found to have less than 92% homology to any of the known sequences in NCBI database, hence possibly represent so far untapped bacterial genus. Based on the microbial diversity analysis of targeted soils, the phylum level and class level diversity of the targeted soil samples was deciphered. A 16S rRNA gene sequence based phylogenetic analysis of the unculturable microbial communities of representative soils of plateau region of Baramati have been created and resulting dendrogramscould serve for preliminary background information for attempting the cultureof novel unculturable bacteria. This investigation will pave the way for future work on mining of functional genes implicated in salttolerance.
|
NCBI GenBank Accession no |
Nearest valid taxon |
% sequence similarity |
|---|---|---|
|
KJ561578 |
Nostocsp |
97% |
|
KJ561579 |
Gaiellaoccuta |
89% |
|
KJ561580 |
Bacillus songklensis |
99% |
|
KJ561581 |
Physelicystisflava |
91% |
|
KJ561582 |
Arenimonasmalthae |
98% |
|
KJ561583 |
Pseodomonas alcaligenes |
99% |
|
KJ561584 |
Halophagafoetida |
83% |
|
KJ561585 |
Candidatus methylomibillis |
83% |
|
KJ638401 |
Devosiainsululae |
97% |
|
KJ638402 |
Herbaspirillum seropedicae |
97% |
|
KJ638403 |
Bacillus songklenis |
99% |
|
KJ638404 |
Arenomionasmetalli |
98% |
|
KJ638405 |
Pseudomonas alcaligenes |
98% |
|
KJ638406 |
Chondromyces apiculatus |
92% |
|
KJ638407 |
Cesiribacter andamanesis |
89% |
|
KJ638408 |
Derxia gummosa |
97% |
- Techniques to obviate edaphic stresses in orchards grown on shallow basaltic soils
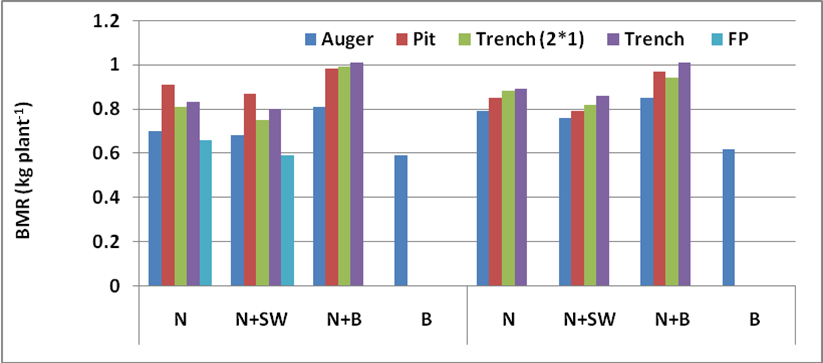
Shallow basaltic soils exist on large scale in Maharashtra and the growth of orchards is largely hampered by hard murrum. Studied the effect of various planting methods and soil mixtures on performance of fruit plants viz., sapota, pomegranate and guava under these conditions. The tallest plant height was recorded in case of pit and trench planting filled up with mixture of native murrum and black soil. Overall, the mixtures of soil with micro-blasting and planted either in trench or pit performed better than all other treatments.

- Influence of chemicals application on onion recovery under varying duration of waterlogging
Experiment was conducted during August 2015 to study the impact of duration of water logging on physiological manifestation and yield of late kharif growing onion var. Bhima Shakti. Six different flooding viz., 0, 2, 4, and 6 days were imposed 15 days after transplanting of onion. Soil and foliar application of chemicals were tried. The results indicated that under normal condition additional nutrient application has significant effect in increasing bulb weight and over all yields irrespective of mode of application over control. Water logging up to 2 days did not have much influence on decreasing the yield of the plant. The plants recovered well with the applied nutrients. However, the effect was predominant with foliar application of KNO3 and spermidine.
Water logging beyond four days drastically reduced the yield. The plant recovery after six days of pounding seems minimal. Nonetheless, with the application of chemicals, the yield improved at least 10-15%. Thick neck bulb occurrence was more as the days of water pounding increased. This was significantly reduced with foliar and soil application of chemicals. The improvement was much better with foliar application of KNO3, spermidine and thiourea whereas sulphur and K application along with humic acid through soil performed better than N application. N soil application negatively influenced some of the quality and bulb parameters. Sporadic flowering and thick neck bulb percentage was increased. TSS content decreased with the increase in water logging. This ultimately decreased the pungency of the bulb which was reflected through decrease in pyruvic acid content. However, this could be negated with the foliar application KNO3.
- An improved reagent based method for phyllosphere community DNA extraction
The culture independent approaches are being widely used in combination with the high throughput sequencing technology that promotes the systematic evaluation of the genetic miscellany of microbial-ecology of different habitats. However, the occurrence of PCR inhibitors in the metagenomic DNA has been frequent in the extraction protocol that restricts the further study to a significant extent. It is therefore needful to make available good quality DNA, particularly free from PCR inhibitors and the contaminating host DNA. Considering these problems, we developed an efficient reagent system consisting of urea, NaCl and SDS that is non-destructive to the host and yields good quality DNA.
Standardization of extraction protocol for crude biomolecules from bacterial isolate using XAD-16
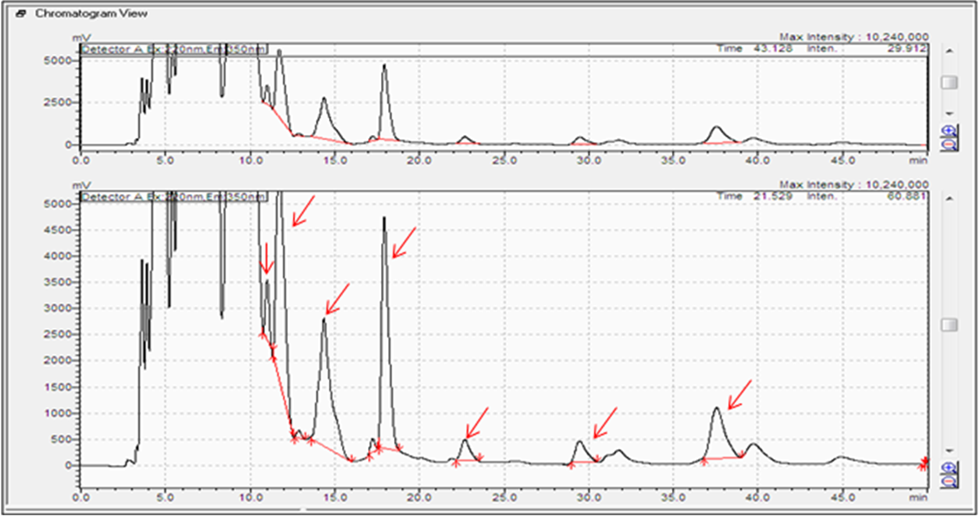
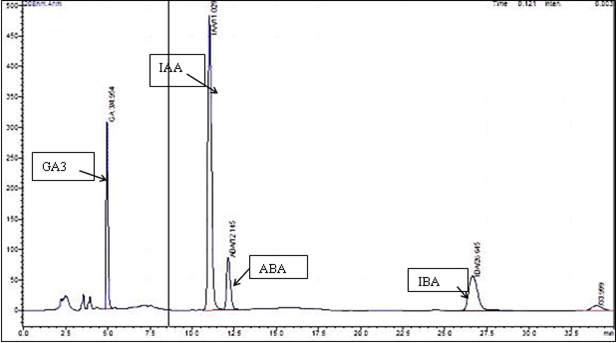
- Standardization of rapid method for quantitative detection of IAA and IBA
Bacterial isolates obtained from different saline soil samples were evaluated for their plantgrowth promotional traits in terms of IAA, Sderophore under simulated drought and salinity stress. At 5% salt concentration, almost all the selected isolates produced higher quantity of IAA;at salt concentration 10% similar effect (lower amount of IAA) was observed as that of 2% where as most of the isolates were unable to produce siderophore at 1% salt concentration; or showing poor response. The siderophore hyperproducers showed peak activity at 5% salt concentration. The isolates 1, 3, 5 and 7 produced siderophores at 1% salt, however same isolates were not capable to elaborate siderophores at 5% salt indicating presence of salt-dependent regulatory mechanism. On the other hand the Maximum IAA was produced by the isolates in absence of PEG. However, the quantity of IAA at 20% PEG found more than that of at 10%. Most of the isolates were unable to produce siderophore at 1% salt concentration; or showing poor response. The siderophore hyper producers showed peak activity at 5% salt concentration. The isolates 1, 3, 5 and 7 produced siderophores at 1% salt; however same isolates were not capable to elaborate siderophores at 5% salt indicating presence of salt-dependent regulatory mechanism. The quantitative assay for these isolated with PEG based simulated water deficit stress to resolve these abilities of the isolates at greater level. The maximum siderophore production in almost all the isolates except D5 and D19 isolates was observed at 10% PEG. The values relatively declined at 0 and 20% where only D5 and D19 were showed more siderophore production. At 30 % none of the isolates showed the production.
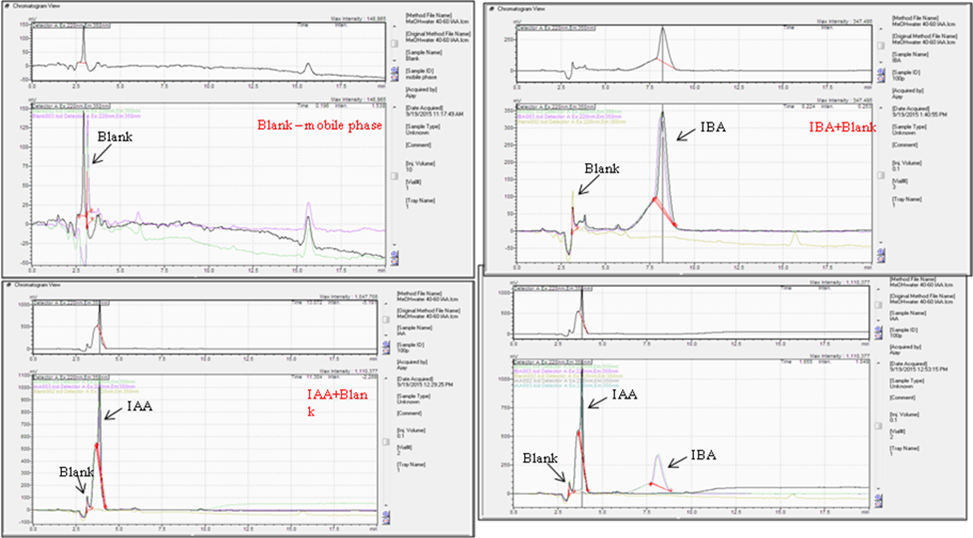
UHPLC based methods for rapid determination of bacterially elaborated biomolecules were developed, mainly for plant-growth hormones. The methods for rapid detection and quantification of IAA, IBA, GA3, Zeatin and ABA were standardized. Using these methods, presence of all the above hormones was successfully determined in the organic extracts of the isolates. The average frequency of plant hormones in the organic extracts of the isolates was IAA > GA3 > IBA > ABA; while the abundance of the hormones found to be IAA > IBA > GA3 > ABA in the tested isolates. Further, the method for metabolite profiling has also been developed to resolve the fine aspects of bacterial metabolic diversity under different stress situations. This method successfully resolved the differences within the organic extracts of single isolate cultivated under varying stresses.
- Nutri-remediation for mitigation of multiple stressors
The lecithin and pyridoxine are acts as nutraceuticals and responsible for mitigation of multiple abiotic stresses. The water-soluble vitamin pyridoxine against stress was evaluated in milkfish, Chanos chanos exposed to endosulfan. The effect of dietary pyridoxine supplementation was studied in terms of antioxidative enzymes (catalase, superoxide dismutase, glutathione-S-transferase), stress markers (HSP 70, caspase-3, cortisol, acetylcholine esterase (AChE), blood glucose, immuno-haematological parameters (total protein, albumin, globulin and A/G ratio, nitroblue tetrazolium, RBC, WBC, Hb), gill histopathology and a subsequent challenge study with Vibrio parahaemolyticus. The lecithin and pyridoxine also enhanced the thermal tolerance of Milkfish and also regulate the mechanism to control the antioxidative status as well as neurotransmitter enzyme. Fish fed the diet supplemented with different composition of lecithin and pyridoxine found to restore towards normal during multiple stressors. Results obtained from this study proved that lecithin and pyridoxine has a definitive role in the mitigation of the multiple abiotic stresses.
- Integrated Agri-aquaculture
ICAR-National Institute of Abiotic Stress Management, Baramati has successfully implemented improved technology interventions in field and horticulture crops, dairy, poultry and fish farming, and Integrated farming in various villages of Navapur Tehsil in Nandurbar District for improving the livelihood of resource poor farmers as part of Tribal Sub-Plan (TSP).